25 Jan OS1 vs OS2 Fiber: What’s the Real Difference?
OS1 vs OS2 Fiber: What’s the Real Difference?
Technical guide for telecom engineers and fiber infrastructure planners
Understanding the difference between OS1 vs OS2 fiber is essential when designing fiber optic networks. Both OS1 and OS2 are single-mode optical fibers, but they differ primarily in attenuation characteristics and deployment environment.
Technical guide for telecom engineers and fiber infrastructure planners
Understanding the difference between OS1 and OS2 fiber is essential when designing fiber optic networks. Both OS1 and OS2 are single-mode optical fibers, but they differ primarily in attenuation performance and application environment.
What Is OS1 Fiber?
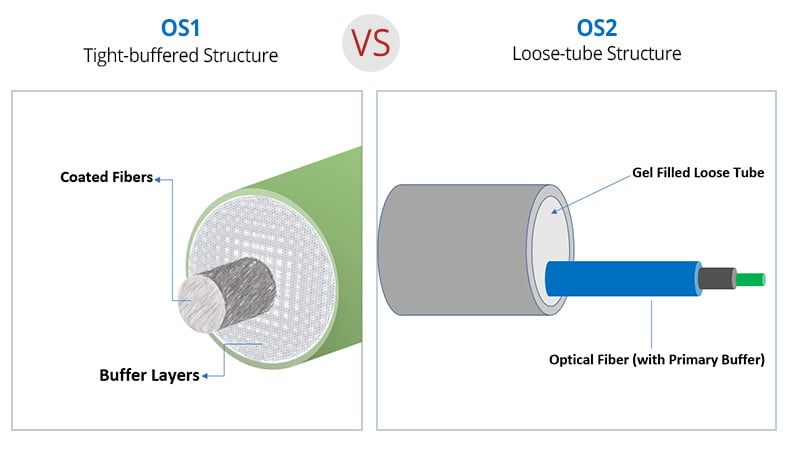
OS1 fiber is a type of single-mode optical fiber typically used in indoor applications such as buildings, campuses, and data centers. It is commonly manufactured in a tight-buffered cable construction.
- Typical attenuation: ≤ 1.0 dB/km
- Core diameter: ~9 µm
- Application: indoor backbone and structured cabling
- Cable type: tight-buffered
OS1 fiber is designed for controlled environments where the cable is protected from moisture, UV exposure, and temperature variation.
What Is OS2 Fiber?
OS2 fiber is a low-attenuation single-mode fiber optimized for outdoor and long-distance transmission. It is typically used in loose-tube or blown fiber cable constructions.
- Typical attenuation: ≤ 0.4 dB/km
- Core diameter: ~9 µm
- Application: FTTx, metro, backbone networks
- Cable type: loose-tube or microduct cable
OS2 fiber complies with ITU-T G.652.D and is the standard fiber type used in modern telecom infrastructure.
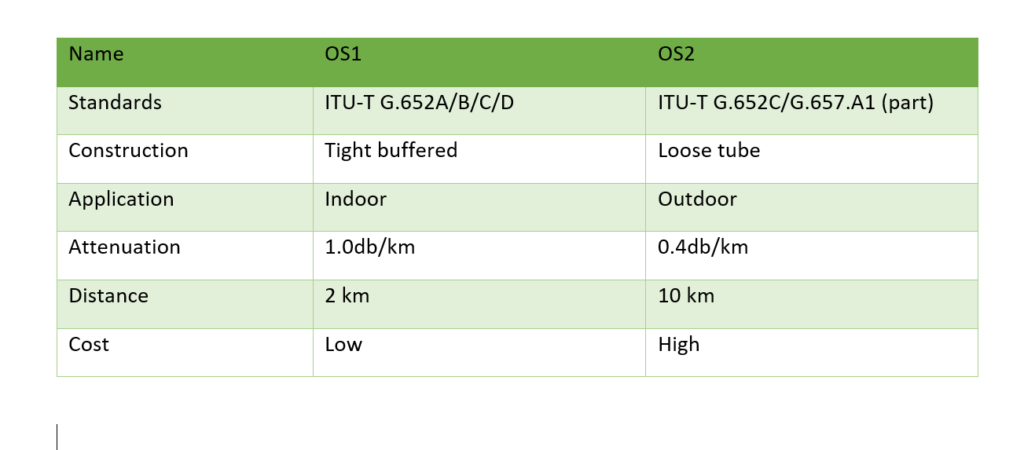
OS1 vs OS2 Fiber Comparison
| Parameter | OS1 | OS2 |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Single-mode | Single-mode |
| Attenuation | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Use | Indoor | Outdoor / long distance |
| Cable Construction | Tight-buffered | Loose-tube / blown |
| Transmission Distance | Shorter | Longer |
Why OS2 Is Preferred in Modern Networks
Today, most telecom and FTTH deployments use OS2 fiber because its low attenuation enables longer installation distances and fewer splice points.
OS2 fiber is particularly suitable for:
- FTTH networks
- Metro fiber infrastructure
- Long-distance backbone links
- Microduct and cable blowing installations
FTTH installation technologies
To understand the broader role of fiber infrastructure in modern connectivity, read: How fiber optic cables and the internet affect our lives .
Cable Blowing and OS2 Fiber Deployment
Modern microduct and cable blowing installations are designed primarily for OS2 fiber cables. Low-friction ducts and air-blown installation methods enable long continuous installation distances with minimal cable stress.
Cable Blowing Machine for OS2 fiber installation
For optical fiber standards reference, see the Fiber Optic Association technical guide .
Conclusion
Both OS1 and OS2 are single-mode fibers with similar core dimensions, but OS2 fiber offers significantly better attenuation performance and environmental durability. For this reason, OS2 fiber has become the default choice for modern telecom and FTTH infrastructure.